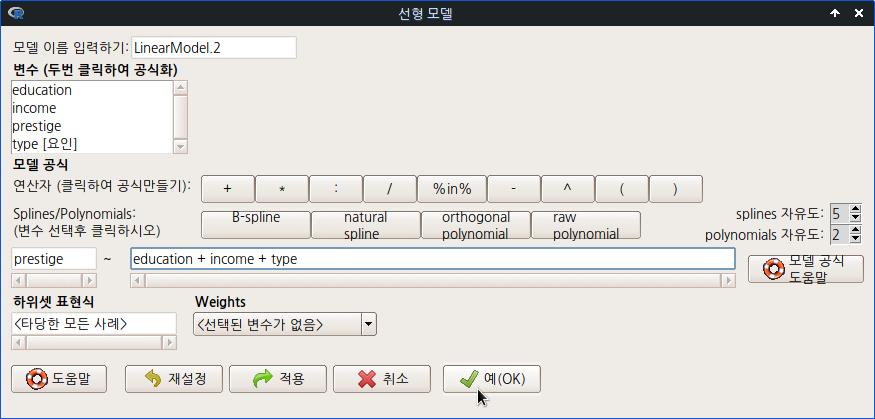
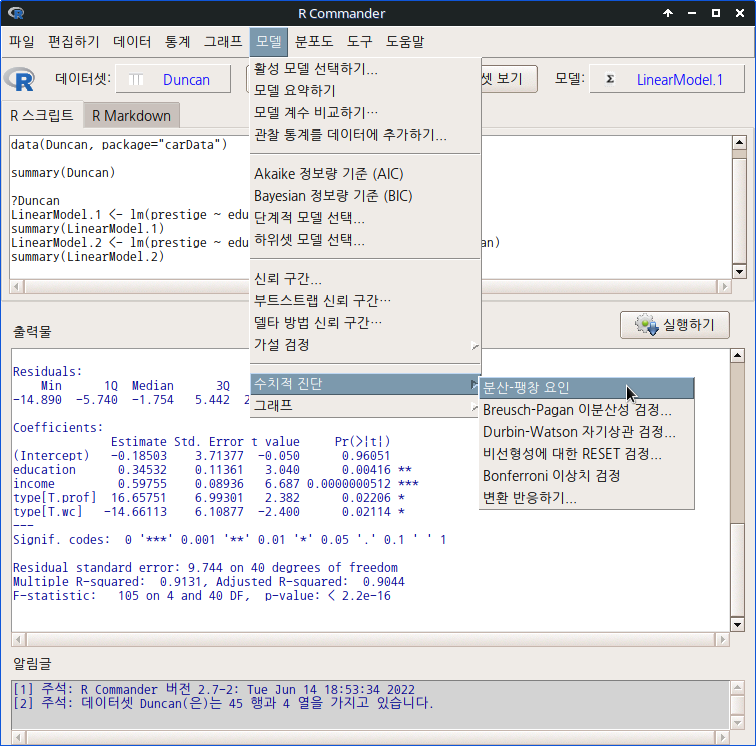
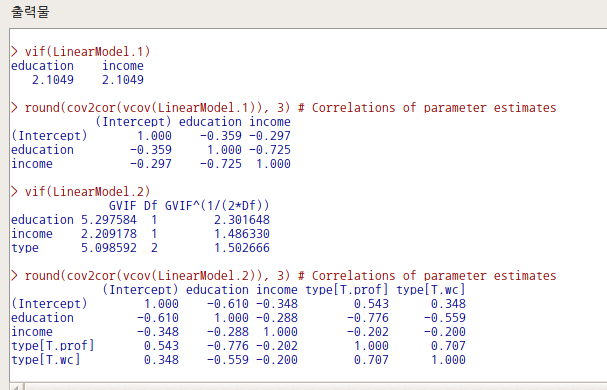
carData::Duncan()
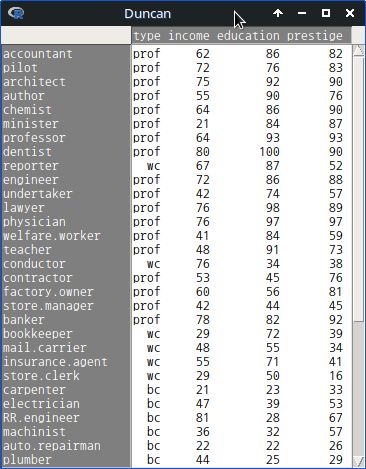
data(Duncan, package="carData")R Commander의 상단에 있는 '데이터셋 보기' 버튼을 누르면, 아래와 같이 데이터셋 내부를 볼 수 있다.
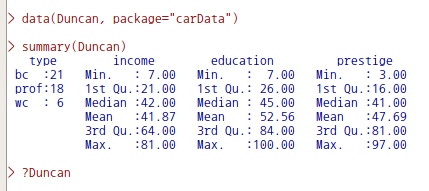
?Duncan # Duncan 데이터셋 도움말 보기| Duncan {carData} | R Documentation |
Duncan's Occupational Prestige Data
Description
The Duncan data frame has 45 rows and 4 columns. Data on the prestige and other characteristics of 45 U. S. occupations in 1950.
Usage
Duncan
Format
This data frame contains the following columns:
type
Type of occupation. A factor with the following levels: prof, professional and managerial; wc, white-collar; bc, blue-collar.
income
Percentage of occupational incumbents in the 1950 US Census who earned $3,500 or more per year (about $36,000 in 2017 US dollars).
education
Percentage of occupational incumbents in 1950 who were high school graduates (which, were we cynical, we would say is roughly equivalent to a PhD in 2017)
prestige
Percentage of respondents in a social survey who rated the occupation as “good” or better in prestige
Source
Duncan, O. D. (1961) A socioeconomic index for all occupations. In Reiss, A. J., Jr. (Ed.) Occupations and Social Status. Free Press [Table VI-1].
References
Fox, J. (2016) Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models, Third Edition. Sage.
Fox, J. and Weisberg, S. (2019) An R Companion to Applied Regression, Third Edition, Sage.